Keeping robotics safe in the packaging industry
June 17, 2014
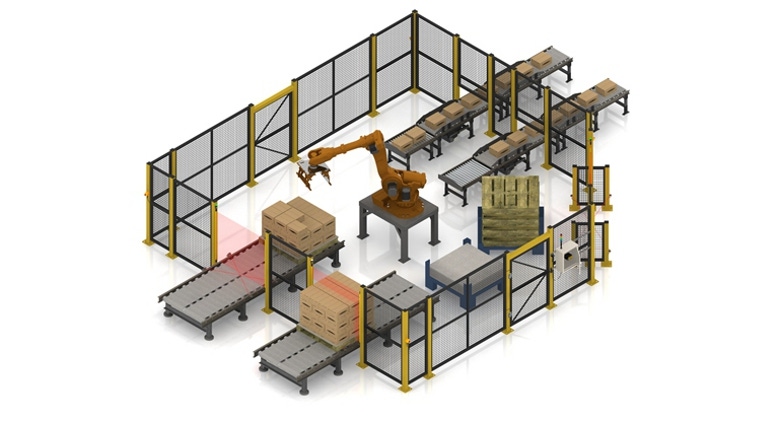
While robotic technology has been around for several years, and used in applications ranging from material handling and assembly to dispensing and processing, it has been slow to gain the popularity it sees today.
According to the business intelligence study, “Trends in Robotics Market Assessment 2014,” by PMMI, The Assn for Packaging and Processing Technologies, more manufacturing companies are investing in robotic technology because of its impact on creating new jobs, greater safety and increased productivity. In fact, the use of robotics today has grown from only 20 percent in 2008 to 75 percent.
With technological advancements, reduced costs and increased ease of use, robotic technology has experienced widespread adoption in many industrial automation applications.
Past to present
Robotics have been widely used in the packaging industry, due to their reliability and accuracy. However, historically, robots were used for palletizing and case packing. With advances in technology, robots are expanding upstream to primary packaging functions, like pick-and-place operations and cartoning applications, and processing tasks, such as cutting and coating.
According to the 2014 PMMI study, respondents anticipate robotics will redefine manufacturing operations by enabling direct contact with food, enhanced spatial awareness of workers, greater precision and sort functions, and faster speeds and heavier lifting capacities.
With a more significant role than ever before, implementing safety measures is vital to ensuring robotics’ continuous operation and optimal performance in packaging operations.
Safety first
Robotics has changed the packaging industry’s safeguarding needs. A one-size-fits-all safety solution will no longer work for the next generation of packaging machines. A variety of devices should be considered, such as safety controllers, safety light curtains and safety laser scanners, to ensure robots are completely secure and to reduce disruption to production.
As robotic packaging systems grow in scale and flexibility—and become more integrated with packaging lines—enhanced safeguarding measures and better operator communication is needed.
In the past, safeguarding scenarios in the packaging industry followed basic conditional “If X, then Y” logic. Simple safety modules and guard monitoring controllers could meet the demands of most packaging operations. With the introduction of flexible robots—where a robot may have access to multiple lines or responsibilities to perform more than one task—safeguarding measures becomes more complex.
Safety controller: A single robot with the ability to function in multiple areas requires multiple safeguards, like e-stop buttons, light curtains and guard switches. In addition, these different functions need to be able to operate independently of one another and in conjunction with one another.
Safety controllers provide an integrated approach to risk reduction by managing the operation of multiple safety devices. For example, if a machine has an emergency stop button, two-hand control, safety light screens and interlocked guard switches, a safety controller can be used to manage all of these operations at a fraction of the cost of multiple safety modules or safety PLCs. Safety controllers can also provide several safety related functions, such as muting or bypassing a safety light screen, external device monitoring (EDM), monitored manual reset functions and logical functions to create separate zones and conditional logic
Visual status indication: With robots and humans in such close working proximity, it’s critical to keep everyone aware of safeguarding status. One fast growing trend is to visually indicate safety status. Emergency stop push buttons, gate interlocks and safety rope pulls are lighting up to communicate armed, actuated and stop conditions.
E-stop buttons with an illuminated base can glow yellow to indicate the machine is enabled or red to indicate stop condition has been initiated. Status indication not only protects workers, but is also useful in identifying issues with the packaging line—especially when a series of buttons have been connected. The visual status indication will let operators know which button was pushed and help them quickly determine where the issue began and enable workers to quickly resolve issues and get the line running again.
Optical safeguarding technologies: When robots become integrated further upstream from the packaging line, it increases the likelihood that robots will work side-by-side with humans. To keep workers protected without introducing clumsy physical barriers, optical safeguarding technologies are an optimal safeguarding solution for robotic packaging applications.
Safety light curtains: When robots are performing multiple tasks or supporting multiple production lines, various entry points to the robotic cell are present. For example, a palletizing robot cell will have access points where cases, new pallets and slip-sheets enter, and where full pallets exit the cell. Safety light curtains can efficiently safeguard several access points with minimal disruption. By selectively muting safety light curtains, pallets and product are allowed to flow in and out of the cell, while personnel is prevented from entering the hazardous area.
Safety laser scanner: A safety laser scanner uses pulsed laser light to scan its surroundings, and then compares the scanned information to its predefined zones. If the scanner detects an intrusion into the robots working area—like a human—it sends a stop signal to the guarded machine.
Area laser scanners are versatile and non-intrusive safeguards. Unlike hard guards, such as fences or safety floor mats, the laser scanner works without physical barriers. Safety laser scanners are also an ideal solution for niche packaging applications where a safety light curtain does not cover the area efficiently.
Washdown-rated devices: As robotics enter the processing and primary packaging areas, they come in contact with food, pharmaceuticals and other regulated materials that require frequent washdowns. These robots need to be guarded by IP67 and IP69K-rated safeguarding devices. Washdown safety light curtains, e-stops and door interlocks are becoming more prevalent in the packaging industry.
Applying safety measures
Safeguarding a robotic palletizer: When safeguarding a robotic palletizer, there are several safety functions involved. For example, the safety device status needs to be communicated to operators. Status monitoring ensures everything is running smoothly and no safety hazards exist.
A safeguarding solution is needed to control safety light curtains with muting, gate switches and E-stop buttons. The solution also needs to safeguard two conveyors going out, two case infeeds and a forklift entry where empty pallets arrive.
A programmable safety controller can manage all of the safety devices with one module, communicating the status of safety devices via Ethernet IP and controlling a tower light for visual indication of safety device statuses.
Safeguarding an inspection station: To inspect robotic results, operators need to be able to access materials without compromising safety. Consider a robot engaged in a pick-and place operation, where the robot places goods in a package as it moves along a conveyor, and an operator then inspects the materials to ensure the package is correct.
By defining tiered safety zones and using area lasers scanners, manufacturers can safeguard their employees from robotic injury without shutting down production lines. When operators enter a pre-specified warning zone, a safety laser scanner recognizes that activity; sends a signal to the robot to limit its movement and an operator signal that says, “you’re in the warning zone, proceed with caution.” If the operator continues into a protective field, the same laser scanner can indentify that movement and signal a complete shutdown. This approach allows the operator to be in close proximity to the robot, without compromising his or her safety or shutting down the packaging line.
Safety mats can also fulfill this purpose, but they are costly and wear out quickly. Other machine safeguarding options include protective barriers and gates, which effectively safeguard an area, but limit the operator’s access.
Looking ahead
As advancements in robotic technology continue to grow, packaging operations will require additional safeguarding methodologies. In order to achieve enhanced efficiency, streamline production and maximize the bottom line with robots, safety measures will be vital to protecting operations against unexpected shutdowns and to keep workers safe.
Mark Lampert, MBA, has more than seven years experience serving the consumer packaged goods (CPG) industries. He is a business development manager at Banner Engineering with expertise in selling sensing, lighting and safety devices for factory automation.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


