Shifting from intention to action on recycled-content packaging
April 30, 2019
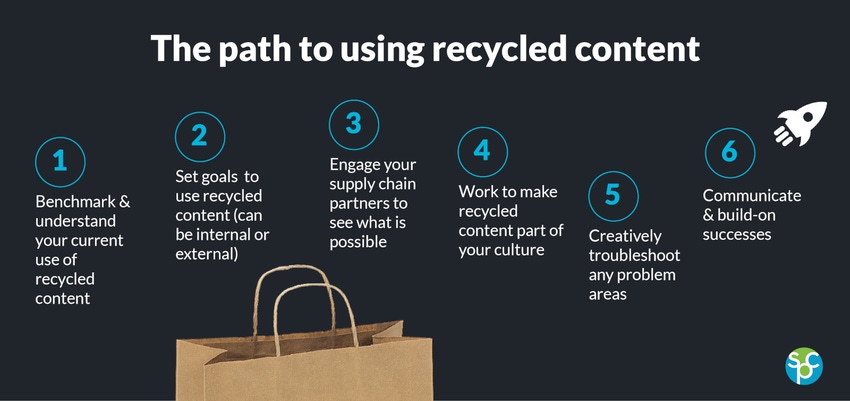
Recycled content is quickly catching on as a core part of a company’s overall sustainable packaging strategy—as well as a key strategy in improving and restoring confidence in the recycling system. For brands and suppliers embarking on the recycled content journey, the Sustainable Packaging Coalition’s new Design for Recycled Content Guide offers actionable insights and practical guidance.
We’ve all heard it at this point, the story of the China imports ban and struggling global recycling markets. This message now appears more frequently in mainstream media and the public is aware of the problem. Restoring faith in our recycling system and investing in its future depends on strong and consistent market demand for recycled materials, which depends on manufacturers using recycled content in their products and packaging.
Numerous laws and organizations’ commitments call upon industry to pursue increased use of recycled content:
• The Circular Economy Directive in Europe is calling for new extended producer responsibility (EPR) fees and exploring fee modulation based around the amount of recycled content.
• The New Plastics Economy Global Commitment calls for its signatories to “circulate the plastic produced, by significantly increasing the amounts of plastics reused or recycled and made into new packaging or products.”
• The UK Plastics Pact commits to have 30% recycled content across all packaging. France and the Netherlands just came out with similar commitments.
The timing is ripe to actively pursue recycled content strategies. The intentions are there, with many brands pledging to create demand for recycled materials by setting their own corporate goals for including more recycled content in their packaging. In the SPC’s recently launched Goals Database, we found that the number of companies making either a concrete goal or a soft commitment in recycled content usage is more than any other goal category, about 62%.
But after the goals are set, practical guidance is needed to help turn industry from intention toward action. The new Design for Recycled Content Guide serves as an important tool in a companies’ recycled content journey, offering insights on topics such as supply and demand, performance, processing, aesthetics, design, cost and strategies for success to deal with diverse challenges across material types.
The Sustainable Packaging Coalition conducted interviews with material manufacturers, packaging converters, brand owners, and retailers, collecting stories on how they navigate challenges and achieved successes. Success stories are peppered throughout the Guide.
The scope of the SPC’s Design Guide includes plastic, paper, glass and metal (aluminum and steel), all of which have very different stories and considerations.
Plastics
In general, only high grades of recycled plastics have significant demand—like clear polyethylene terephthalate (PET) suitable for food contact, and natural colored high-density polyethylene (HDPE)—and there is not enough supply available on the market to meet current demand for these materials.
Other types of recycled plastics (resin identification codes 3 through 7) lack both quality supply and demand. For the supply that is available, there are issues of cost competitiveness to virgin plastics.

Seventh Generation is an example of a company that has successfully navigated many of the challenges associated with using recycled plastics. The company began with HDPE and has progressed to almost 100% recycled content in most of its HDPE and PET bottles today. The company has now brought polypropylene closures made of 100% recycled content to the market and recently launched some of the first flip-top closures made of 100% recycled polypropylene. Seventh Generation is also exploring the use of recycled polyethylene in low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films. It has achieved all of this in part by switching from cost savings in its product portfolio to investing in packaging sustainability.
Paper
Paper is unique in this conversation because it comes from a renewable resource that, when responsibly managed, can also be a sustainable sourcing strategy. While virgin fiber will always be needed, using recycled fiber supports recycling markets and is appropriate for certain types of packaging.
Overall demand for recycled fiber for use in paper packaging is generally believed to exceed supply. The supply of recycled fiber is constrained, in part, by the number and capacity of recycled paper mills. Lush is an example of a company that has navigated this challenge by developing long-term relationships with dedicated recycled paper suppliers to find recycled fiber that works for its packages.

Glass
Unlike paper or plastics, glass does not degrade. Its constraint is mainly in collection and the fact that supply availability is regional, since glass is heavy and transportation costs are high. Diageo’s Glass is Good recycling program in Brazil encourages bars, restaurants and other customers to sign up to have their used glass containers collected for recycling. The sorted glass is then transported to Glass is Good grinding sites, set up and run by local cooperatives, who grind it into cullet and store it.
Aluminum
The specific amount of recycled aluminum in a given package is largely unknown, due to how aluminum supply chains are structured and the availability of recycled aluminum at the time a batch is made. Past efforts to market cans with consistent, high levels of recycled aluminum encountered barriers, including brand owners’ resistance to committing to a single supplier of cans, even if it meant guaranteed and verified high levels of recycled aluminum. In the case of aluminum, brand owners can help encourage a system in which more recycled aluminum usage is tracked and verified.
Working across the supply chain is vital to successfully increasing the demand for recycled content in packaging, no matter the material. The SPC Guide sets out recommendations for brands, as well as suppliers.
While there is much momentum around recycled content in packaging currently, there is still a long journey ahead until this sourcing option becomes mainstream. Our hope is that the Design for Recycled Content Guide will help brands and suppliers that are starting off on this journey. It is a living document, and we hope that you will help us build it by adding your story and updating us on your progress and learnings.
In the case of recycled content, we need to learn by doing and collectively work to build these markets, which all industry will benefit from.

Tristanne Davis joined GreenBlue in November 2017 as a project manager with the Sustainable Packaging Coalition (SPC). Her primary work involves helping to shape and deliver on its Industry Leadership Committee initiatives, ASTRX project and Forest Products work. Davis received her BA in economics from Skidmore College followed by several years of environmental consulting for a variety of clients across business and government, and a stint in Nicaragua managing an agroforestry program with a local non-governmental organization (NGO). She recently finished a Master’s program in industrial ecology at the Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies, and an MBA program at IE Business School in Spain.
********************************************************************************
EastPack 2019 (June 11-13) is the region's premier packaging event connecting professionals from companies like PepsiCo, Pepperidge Farms and Mars with suppliers offering the latest packaging technologies, including a range of automation solutions, from semi-automatic equipment to sophisticated "smart" systems. Register to attend today!
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


